
By Shailesh Menon
Nearly 5,000 farmers in Samastipur, Begusarai and Muzzaffarpur districts of Bihar are reaping benefits of a smart decision taken last season. Instead of selling their produce cheap, immediately on harvesting, they warehoused yields and waited for grain prices to appreciate in the off-season. Ergos, a Bengaluru-based startup that offers micro-warehousing, seeded the idea.
“Farmers are forced to sell immediately after harvesting,” says Kishor Kumar Jha, founder-director, Ergos. “With proper warehousing, farmers can store their produce and sell when prices move up.”
The plan seems to be working as maize farmers who have tied up with Ergos have got 20-30% higher prices for their grains a few months ahead of harvest.
The plan seems to be working as maize farmers who have tied up with Ergos have got 20-30% higher prices for their grains a few months ahead of harvest.
What makes Ergos practical and transparent is a mobile phone app, which lists out the stock held by farmers in warehouses and real-time market price of grains. The farmer is certain of his stock in the warehouse, and is also aware of market trends which allow him to set his price.
“It works like shares in demat form,” analogises Jha. “Once the farmer warehouses grains, we grade stock and enter details on the app. The farmer can store grains in good condition and sell his stock when he gets his desired price,” he adds.
Ergos charges Rs 6-12 per quintal (per month) as warehousing-cum-price advisory charges. The post-sale payment (to farmers) is done in four to seven days, Ergos officials claim. For immediate cash requirement, the farmer can use the warehouse receipt to borrow (70-75% loan-to-value) from banks — IDBI and SBI, in this case. Excluding the 24 micro warehouses (with capacities between 200 and 700 tonnes), the mobile app forms the backbone of Ergos’ operations.
There are several other ventures — some work directly with farmers; a fewer still have tied up with farmer producer organisation (FPOs) and NGOs (See Green Fields Stretch Out For Agtech).
“Farmers have begun using smartphones as a tool for information gathering,” says Amit Kar, head of agricultural economics at Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI). “Most service providers now use calls, audio alerts or text messages to communicate with farmers now. This is helpful… But it would be even better when they start communicating with farmers pictorially or through videos,” Kar adds.
THE SMARTPHONE INCURSION
Farmers residing in the hinterlands have started using popular communication apps. “Farmers are using WhatsApp big-time… They’re forming chat groups amongst themselves and sharing information,” affirms GC Shrotriya, national head (VAS), Iffco Kisan Sanchar, which partners with Bharti Airtel to link up with farmers. “Mobiles phones have become an information source for farmers. Apart from getting in touch with agri-service providers and scientists, farmers manage to get answers and solutions communicating with each other,” Shrotriya adds.
Almost all agri-service/agri-tech companies have started mobile apps though call lines are open as farmers are more comfortable with direct personal contact.“Just an app is not good enough; we need people on the field also, to guide and hand-hold farmers. We’ve some 150 employees working with farmers across the country,” says Rajiv Tevtiya, CEO at RML AgTech. “Mobiles phones can make farming a viable business. They can bring in efficiency, increase productivity and bridge knowledge gaps,” Tevtiy adds.
Most agri-tech companies operate in the information services space. They proffer weather prediction, mandi rates, trader contact details and government subsidy details. Firms with research labs, in-house agronomists and agri-consultants also bundle advisory services to farmers. RML AgTech, for instance, had alerted their subscribers about a potential rise in wheat, tomato and onion prices, way back in March 2017. “We use a lot of data analytics to arrive at our conclusions. Data science can also be used for crop selection,” Tevtiya adds.
SERVICES OFFERED
Sarthak Tiwari from Kumha village (Saran, Bihar) placed a call to livestock consultants at Iffco Kisan Sanchar, when his cow’s hooves were severely infected. Tiwari had subscribed to Iffco Kisan Sanchar services by taking a designated Airtel connection. “The Iffco doctor prescribed medicines for the cow. I incurred just Rs 130 for some lotion and ointment,” Tiwari told ET. Tiwari also managed to get a “gift”— additional calltime worth Rs 50, by participating in a quiz contest run by Iffco Kisan Sanchar.
Prem Singh Verma in Theog village (Shimla) of Himachal Pradesh got guidance over the phone, to treat “stalk rot disease” in his cauliflower crop. “The agri-consultant advised me to spray insecticide on the leaves… I could save my crop because of their tips,” recollects Verma.
Agri-services companies such as RML AgTech, Indian Agricultural Research Institute’s (IARI) M-Krishi and Handygo Technologies help farmers with queries around plant protection and disease management and especially while sowing.
Many a time, farmers choose the wrong crop in their fields. Take, for instance, how farmers in Maharashtra abandoned tomatoes this year, and grew more pomegranates, resulting in a significant price crash for the latter. Farmers in Himachal Pradesh dumped apples this year for cauliflower, causing the latter’s price to fall by over 50%. “Crop selection has always been a problem… We’re doing this to prevent farmers from planting the same crop across large tracts, without checking soil suitability,” explains Amit Kar at IARI.
Agri-services companies with attached research labs have started advisory services as well. Farmers have to simply click pictures of disease-afflicted crop and send to the labs. Most agri-services companies have dedicated call centres to manage farmer calls. Companies like Handygo employ over 100 consultants during sowing season to help their subscribers.
“Frequency of calls goes up during sowing and plant-growth phase. Most farmers’ queries then are around plant protection and disease management,” says Praveen Rajpal, CEO of Handygo Technologies. “Our consultants advise farmers about new fungicides, fertilisers and insecticides… We also teach them techniques of land preparation, mechanised sowing and seed treatment.”
After harvesting, “farmers face a lot of challenges… We try to solve some of their problems using technology,” says Krishna Kumar, CEO of Cropin. “We give farmers weather and price updates… We can also do crop predictions, land audits and geospatial analysis of crops. We can predict crop output; we can also tell them which part of field is yielding well by looking at satellite images,” Krishna Kumar adds.
Information services help farmers increase yields through better crop management and use of inputs, enabling them to identify the best time and place to sell produce and mark-up incomes.
“Access to reliable and trusted information is creating a huge difference in the way agriculture is done in India,” says Arvind Nevatia, SVP – consumer segment, Vodafone India. The telecom company has an information service package (Vodafone Kisan Mitra) for farmers.
According to a report prepared by Vodafone titled ‘Connecting farmers in India’, close to 62% of Indian farmers own less than one hectare of agricultural land. Companies such as Crofarm procure directly from farmers and sell to food processing majors and small retailers. “We use mobile phones to place our indent for fruits and vegetables. Once we buy, we pay the farmers in 7 to 10 days,” says Varun Khurana, co-founder of Crofarm, which works with farmers in Haryana and UP.
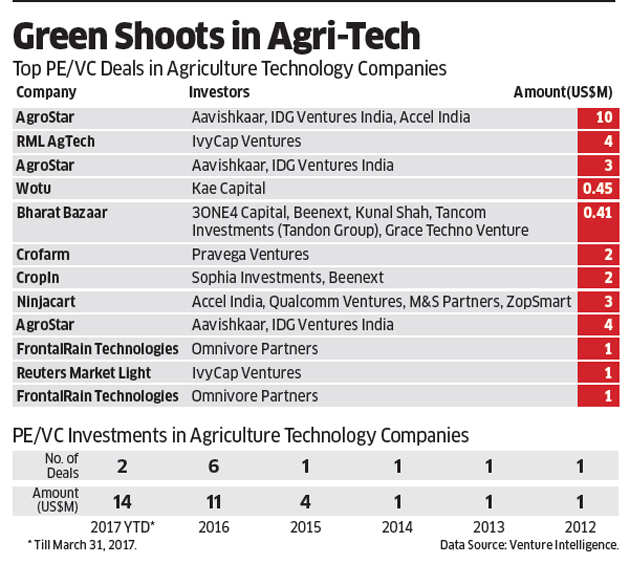
INVESTMENT OPPORTUNITY
Agri-tech and services companies, which use internet and mobile technology to connect with farmers, are seeing investment interest from venture capitalists and private equity funds. “Mobile makes agri-tech / agri-services business more scalable. It can solve a lot of problems that farmers are facing now,” believes Vineet Rai, CEO of Aavishkaar Venture Management. “We’re looking at agri-tech companies that help to reduce input costs (for farmers) and increase productivity.” Agri-related businesses, if stacked against BFSI and ecommerce, take longer time to grow, but they have larger “elbow room” to spread out and diversify. Companies that specialise in farm management software, data analytics and crop prediction, livestock management and plant/crop data analysis have more allure for investors.


Leave a Reply